Empowering Disability Rights and Fostering Inclusion: Building an Inclusive Society for All
Disability rights and inclusion are essential aspects of creating a just and equitable society that values the dignity and worth of every individual. Ethical considerations play a crucial role in shaping our approach to disability rights, guiding us in ensuring equal opportunities, accessibility, and full participation for persons with disabilities. In this article, we will explore the importance of ethics in promoting disability rights and inclusion, provide an example that highlights ethical challenges, and discuss strategies to address these challenges and create a more inclusive society while upholding ethical principles.
Ethics in Disability Rights and Inclusion
Ethics serves as a foundation for advocating and protecting the rights of individuals with disabilities. It encompasses principles such as respect for autonomy, non-discrimination, dignity, and the promotion of well-being. By incorporating ethical considerations, we can challenge societal attitudes and barriers that perpetuate exclusion, discrimination, and unequal treatment of persons with disabilities.
Understanding Disability Rights and Inclusion
Disability rights refer to the legal and moral entitlements of individuals with disabilities to live with dignity, equality, and autonomy. Inclusion involves creating environments, policies, and practices that welcome and value the participation of individuals with disabilities in all aspects of life, ensuring they have equal access to education, employment, healthcare, transportation, and social opportunities.
Example
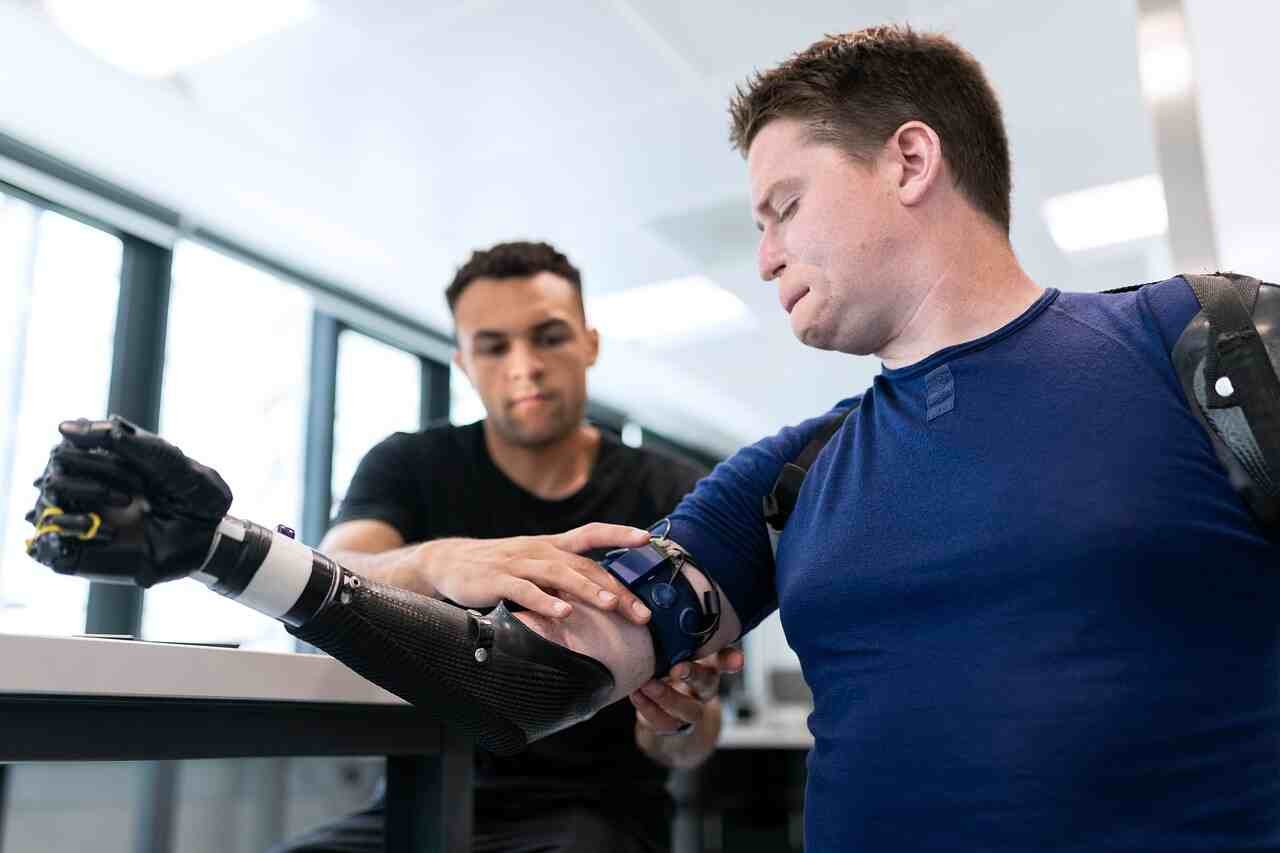
One ethical challenge in disability rights and inclusion is the lack of accessibility in the physical environment. When public spaces, transportation systems, workplaces, and educational institutions are not designed to accommodate individuals with disabilities, it hinders their participation and limits their opportunities. Ethical considerations compel us to prioritize universal design and accessibility, ensuring that everyone, regardless of their abilities, can fully engage and navigate their surroundings with dignity and independence. This includes implementing ramps, elevators, Braille signage, captioning, and assistive technologies to create inclusive environments.
The Ethical Imperative
At the heart of disability rights and inclusion lies a strong ethical imperative. Ethical considerations such as respect for autonomy, equality, non-discrimination, and social justice compel us to challenge the barriers and biases that limit the opportunities and experiences of individuals with disabilities. Upholding ethical principles guides us in working towards a more inclusive society that acknowledges and embraces the diversity of human capabilities.
Promoting Disability Rights and Inclusion
Legislation and Policy
Robust legislation and policy frameworks are essential for protecting and promoting disability rights. Laws that enforce accessibility standards, prohibit discrimination, and ensure reasonable accommodations are crucial steps towards an inclusive society. Regular review and amendment of existing laws can address emerging challenges and ensure the continual progress of disability rights.
Education and Awareness
Education plays a pivotal role in fostering inclusion. By promoting disability awareness and educating society about the rights, capabilities, and contributions of individuals with disabilities, we can challenge stereotypes, reduce stigma, and foster empathy and understanding. Educational institutions should embrace inclusive practices that cater to diverse learning needs.
Education plays a pivotal role in promoting inclusion and combating discrimination. Incorporating disability awareness and inclusive education into school curricula can help challenge misconceptions, reduce stigma, and nurture a more inclusive and accepting society.
Accessibility and Universal Design
Ensuring accessibility in physical infrastructure, information, communication, and technology is vital for inclusion. Universal design principles should be applied to create environments that accommodate individuals of all abilities. This includes accessible transportation, buildings, websites, and assistive technologies that empower individuals with disabilities to navigate their surroundings independently.
Employment Opportunities
Promoting inclusive employment practices is crucial for fostering independence and empowerment. Employers should embrace diversity, provide reasonable accommodations, and create accessible workplaces that allow individuals with disabilities to contribute their skills and talents. Encouraging inclusive recruitment, training, and advancement opportunities can help break down barriers to employment.
Providing equal employment opportunities for individuals with disabilities is vital for their economic empowerment and social inclusion. Employers should implement inclusive hiring practices, provide reasonable accommodations, and foster a supportive and accessible work environment that values diversity and promotes equality.
Support Services and Empowerment
Accessible support services, such as healthcare, rehabilitation, counseling, and independent living programs, are essential for empowering individuals with disabilities. These services enable individuals to develop their potential, enhance their quality of life, and actively participate in society. Collaboration between government agencies, service providers, and community organizations is key to ensuring comprehensive support systems.
Shifting Attitudes and Mindsets
Creating a culture of inclusion requires a shift in societal attitudes and mindsets towards individuals with disabilities. By challenging stereotypes, promoting empathy, and fostering understanding, we can break down barriers and cultivate a society that values the contributions and abilities of all individuals.
Advocacy and Policy Reform
Engaging in advocacy efforts and advocating for policy reforms is crucial to advancing disability rights and inclusion. Collaborating with disability rights organizations, policymakers, and community stakeholders can bring about positive change in legislation, ensuring the protection of rights and the implementation of inclusive practices.
Accessible Environments
Creating accessible physical environments, including infrastructure, public spaces, transportation, and buildings, is essential for fostering inclusion. Universal design principles should be integrated from the outset, ensuring that environments are accessible to all individuals, regardless of their abilities.
Collaborative Partnerships
Building partnerships between government agencies, disability rights organizations, advocacy groups, and community stakeholders is crucial for driving change. By working collaboratively, sharing resources, and exchanging knowledge, we can leverage collective expertise to address barriers, develop inclusive policies, and empower individuals with disabilities.
Resolving Ethical Issues in Disability Rights and Inclusion
Resolving ethical issues in disability rights and inclusion necessitates a multifaceted approach that involves addressing systemic barriers, promoting accessibility and equal opportunities, challenging discriminatory attitudes and practices, fostering inclusive policies, and empowering individuals with disabilities to actively participate in decision-making processes, thus creating a society that values diversity, respects the rights and dignity of all individuals, and ensures that disability is not a barrier to full inclusion and participation in all aspects of life.
- Legislation and Policies: Ethical reform efforts in disability rights and inclusion involve the development and implementation of comprehensive legislation and policies that protect the rights of individuals with disabilities. This includes laws that prohibit discrimination, ensure accessibility, and promote equal opportunities in areas such as employment, education, healthcare, and public services. Strong legal frameworks establish the foundation for an inclusive society.
- Education and Awareness: Promoting education and awareness is essential for fostering a more inclusive society. This involves raising public consciousness about the rights, needs, and capabilities of persons with disabilities, dispelling misconceptions, and challenging stereotypes. By promoting empathy, understanding, and inclusivity from an early age, we can foster a culture that embraces diversity and values the contributions of individuals with disabilities.
- Collaboration and Participation: Meaningful collaboration with organizations, advocates, and individuals with disabilities is crucial in driving ethical reform efforts. Including the voices and perspectives of those directly affected ensures that policies and practices are inclusive, respectful, and responsive to the needs of the community. This collaborative approach fosters empowerment, self-advocacy, and shared decision-making.
- Accessible Design and Infrastructure: Ethical considerations call for the prioritization of universal design principles in the planning and construction of infrastructure. This includes ensuring accessible public transportation, barrier-free environments, inclusive technology, and communication tools that cater to diverse needs. By incorporating accessibility from the outset, we create a more inclusive and equitable society for all.
- Supportive Services and Resources: Ethical reform efforts also involve providing necessary support services and resources to individuals with disabilities. This includes access to healthcare, rehabilitation services, assistive devices, and reasonable accommodations in the workplace or educational settings. By removing barriers and providing adequate support, we empower individuals with disabilities to fully participate in society and reach their full potential.
- Education and Sensitization: Educating society about disability rights and promoting disability awareness is crucial. By fostering empathy, understanding, and sensitivity, we can challenge biases, stereotypes, and stigmas surrounding disability, thus paving the way for a more inclusive society.
- Collaboration and Participation: Ethical reform efforts necessitate the active involvement of individuals with disabilities, disability rights organizations, policymakers, and other stakeholders. Collaborative decision-making processes ensure that the voices of those directly affected are heard, and their perspectives inform policy changes and initiatives.
- Advocacy and Legal Frameworks: Advocacy plays a significant role in driving ethical reforms. By advocating for stronger legal frameworks that protect the rights of individuals with disabilities and ensure their inclusion in all aspects of life, we can create a more just and equitable society.
- Accessibility and Universal Design: Emphasizing accessibility and universal design is essential for promoting ethical practices in disability rights and inclusion. Ensuring that physical environments, information, communication, and technology are accessible to all individuals, regardless of their abilities, fosters inclusivity and equal opportunities.
- Employment Opportunities: Promoting inclusive employment practices is crucial for ethical disability rights and inclusion. Employers should create accessible work environments, provide reasonable accommodations, and embrace diversity by actively recruiting and hiring individuals with disabilities.
- Empowerment and Support Services: Empowering individuals with disabilities through support services, including counseling, independent living programs, assistive technologies, and vocational training, is vital for ethical reform. These resources enable individuals to maximize their potential, participate fully in society, and lead fulfilling lives.
Conclusion
Promoting disability rights and inclusion requires a commitment to ethical principles that uphold respect, dignity, and equal opportunities for all individuals. By addressing ethical challenges, such as accessibility barriers, through legislation, education, collaboration, inclusive design, and support services, we can create a more inclusive society that embraces diversity and ensures the full participation of persons with disabilities. By valuing the inherent worth and rights of every individual.
Sources: PinterPandai, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, The Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights is the leading United Nations entity
Photo credit: RAEng_Publications via Pixabay