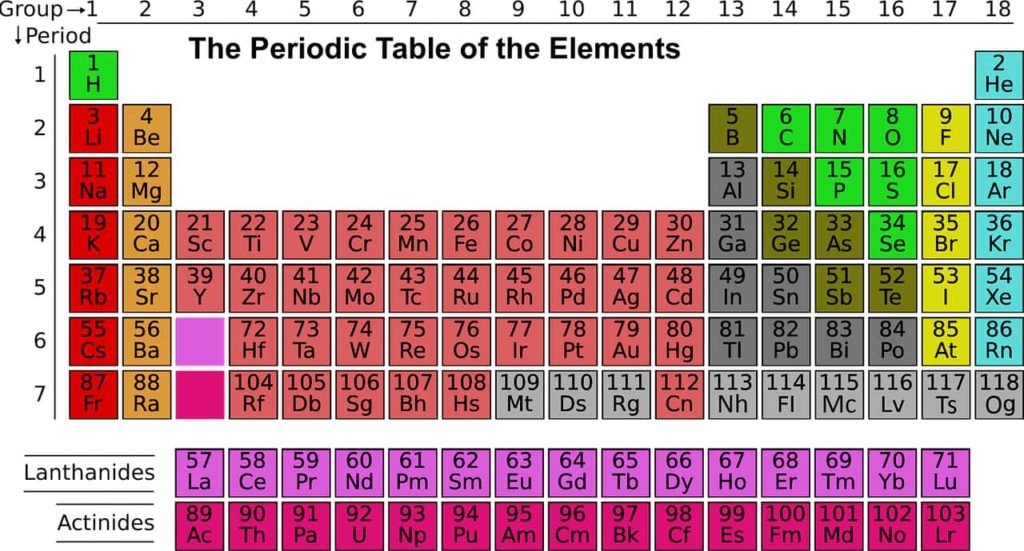
Periodic Table of Elements
The Periodic Table of the Elements, also known as the Table or Mendeleev’s Table, or simply Periodic Table, represents all chemical elements, ordered by increasing atomic number and organized according to their electronic configuration, which underlies their chemical properties.
The design of this table is generally attributed to the Russian chemist Dmitry Ivanovich Mendeleev, who, in 1869, built a table, different from the one used today, but similar in principle, whose great interest was to propose a classification systematic system of elements known at the time in order to underline the periodicity of their chemical properties, to identify the elements which remained to be discovered, even to predict certain properties of chemical elements then unknown.
Read also: Chemistry Studies and Branches (Fields of Chemistry)
The periodic table has undergone many readjustments since then until it takes the form we know it today. It has become a universal repository to which all types of physical and chemical behavior of the elements can be related. Since the IUPAC update of November 28, 2016, its standard form has 118 elements, ranging from 1H hydrogen to 118Og oganesson.
Periodic table
- Ca: 40.078 — Formal short value, rounded (no uncertainty)
- Po: [209] — mass number of the most stable isotope
Since 2016, the periodic table has 118 confirmed elements, from element 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (oganesson). Elements 113, 115, 117 and 118, the most recent discoveries, were officially confirmed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) in December 2015. Their proposed names, nihonium (Nh), moscovium (Mc), tennessine (Ts) and oganesson (Og) respectively, were made official in November 2016 by IUPAC.
The first 94 elements occur naturally; the remaining 24, americium to oganesson (95–118), occur only when synthesized in laboratories. Of the 94 naturally occurring elements, 83 are primordial and 11 occur only in decay chains of primordial elements. No element heavier than einsteinium (element 99) has ever been observed in macroscopic quantities in its pure form, nor has astatine (element 85); francium (element 87) has been only photographed in the form of light emitted from microscopic quantities (300,000 atoms).
Groups
A group or family is a vertical column in the periodic table. Groups usually have more significant periodic trends than periods and blocks. Modern quantum mechanical theories of atomic structure explain group trends by proposing that elements within the same group generally have the same electron configurations in their valence shell. Consequently, elements in the same group tend to have a shared chemistry and exhibit a clear trend in properties with increasing atomic number. In some parts of the periodic table, such as the d-block and the f-block, horizontal similarities can be as important as, or more pronounced than, vertical similarities. Read also: Periodic table block S P D F | The Periodic Table of the Elements
Under an international naming convention, the groups are numbered numerically from 1 to 18 from the leftmost column (the alkali metals) to the rightmost column (the noble gases). Previously, they were known by roman numerals. In America, the roman numerals were followed by either an “A” if the group was in the s- or p-block, or a “B” if the group was in the d-block. The roman numerals used correspond to the last digit of today’s naming convention (e.g. the group 4 elements were group IVB, and the group 14 elements were group IVA). In Europe, the lettering was similar, except that “A” was used if the group was before group 10, and “B” was used for groups including and after group 10. In addition, groups 8, 9 and 10 used to be treated as one triple-sized group, known collectively in both notations as group VIII. In 1988, the new IUPAC naming system was put into use, and the old group names were deprecated.
Elements in the same group tend to show patterns in atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity. From top to bottom in a group, the atomic radii of the elements increase. Since there are more filled energy levels, valence electrons are found farther from the nucleus. From the top, each successive element has a lower ionization energy because it is easier to remove an electron since the atoms are less tightly bound. Similarly, a group has a top-to-bottom decrease in electronegativity due to an increasing distance between valence electrons and the nucleus. There are exceptions to these trends: for example, in group 11, electronegativity increases farther down the group.
| IUPAC group | 1a | 2 | n/a | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mendeleev (I–VIII) | IA | IIA | IIIB | IVB | VB | VIB | VIIB | VIIIB | IB | IIB | IIIB | IVB | VB | VIB | VIIB | b | |||
| CAS (US, A-B-A) | IA | IIA | IIIB | IVB | VB | VIB | VIIB | VIIIB | IB | IIB | IIIA | IVA | VA | VIA | VIIA | VIIIA | |||
| old IUPAC (Europe, A-B) | IA | IIA | IIIA | IVA | VA | VIA | VIIA | VIIIB | IB | IIB | IIIB | IVB | VB | VIB | VIIB | 0 | |||
| Trivial name | H and Alkali metalsr | Alkaline earth metalsr | Coinage metals | Triels | Tetrels | Pnictogensr | Chalcogensr | Halogensr | Noble gasesr | ||||||||||
| Name by elementr | Lithium group | Beryllium group | Scandium group | Titanium group | Vanadium group | Chromium group | Manganese group | Iron group | Cobalt group | Nickel group | Copper group | Zinc group | Boron group | Carbon group | Nitrogen group | Oxygen group | Fluorine group | Helium or Neon group | |
| Period 1 | H | He | |||||||||||||||||
| Period 2 | Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | |||||||||||
| Period 3 | Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | |||||||||||
| Period 4 | K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | |
| Period 5 | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | |
| Period 6 | Cs | Ba | La–Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Period 7 | Fr | Ra | Ac–No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
n/a Do not have a group number
b Group 18, the noble gases, were not discovered at the time of Mendeleev’s original table. Later (1902), Mendeleev accepted the evidence for their existence, and they could be placed in a new “group 0”, consistently and without breaking the periodic table principle.
r Group name as recommended by IUPAC.
| New IUPAC name | CAS name (U.S.) | Name by element |
| Group 1 | IA | lithium family |
| Group 2 | IIA | beryllium family |
| Group 3 | IIIB | scandium family |
| Group 4 | IVB | titanium family |
| Group 5 | VB | vanadium family |
| Group 6 | VIB | chromium family |
| Group 7 | VIIB | manganese family |
| Group 8 | VIIIB | iron family |
| Group 9 | VIIIB | cobalt family |
| Group 10 | VIIIB | nickel family |
| Group 11 | IB | copper family |
| Group 12 | IIB | zinc family |
| Group 13 | IIIA | boron family |
| Group 14 | IVA | carbon family |
| Group 15 | VA | nitrogen family |
| Group 16 | VIA | oxygen family |
| Group 17 | VIIA | fluorine family |
| Group 18 | VIIIA | helium family or neon family |
Periodic Table with Element Names and Electronegativity
This periodic table chart lists elements by name in alphabetical order including the element symbol, atomic number, and Pauling electronegativity value for quick and simple reference.
| Element Name | Symbol | Atomic Number | Atomic Weight | Electronegativity (x) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinium | Ac | 89 | [227] | 1.10 |
| Aluminium | Al | 13 | 26.98 | 1.61 |
| Americium | Am | 95 | [243] | 1.30 |
| Antimony | Sb | 51 | 121.76 | 2.05 |
| Argon | Ar | 18 | 39.95 | |
| Arsenic | As | 33 | 74.92 | 2.18 |
| Astatine | At | 85 | [210] | 2.20 |
| Barium | Ba | 56 | 137.33 | 0.89 |
| Berkelium | Bk | 97 | [247] | 1.30 |
| Beryllium | Be | 4 | 9.012 | 1.57 |
| Bismuth | Bi | 83 | 208.98 | 2.02 |
| Bohrium | Bh | 107 | [270] | |
| Boron | B | 5 | 10.81 | 2.04 |
| Bromine | Br | 35 | 79.9 | 2.96 |
| Cadmium | Cd | 48 | 112.41 | 1.69 |
| Caesium | Cs | 55 | 132.91 | 0.79 |
| Calcium | Ca | 20 | 40.08 | 1.00 |
| Californium | Cf | 98 | [251] | 1.30 |
| Carbon | C | 6 | 12.01 | 2.55 |
| Cerium | Ce | 58 | 140.12 | 1.12 |
| Chlorine | Cl | 17 | 35.45 | 3.16 |
| Chromium | Cr | 24 | 52 | 1.66 |
| Cobalt | Co | 27 | 58.93 | 1.88 |
| Copernicium | Cn | 112 | [285] | |
| Copper | Cu | 29 | 63.55 | 1.90 |
| Curium | Cm | 96 | [247] | 1.30 |
| Darmstadtium | Ds | 110 | [281] | |
| Dubnium | Db | 105 | [268] | |
| Dysprosium | Dy | 66 | 162.5 | 1.22 |
| Einsteinium | Es | 99 | [252] | 1.30 |
| Erbium | Er | 68 | 167.26 | 1.24 |
| Europium | Eu | 63 | 151.96 | |
| Fermium | Fm | 100 | [257] | 1.30 |
| Flerovium | Fl | 114 | [289] | |
| Fluorine | F | 9 | 19 | 3.98 |
| Francium | Fr | 87 | [223] | 0.70 |
| Gadolinium | Gd | 64 | 157.25 | 1.20 |
| Gallium | Ga | 31 | 69.72 | 1.81 |
| Germanium | Ge | 32 | 72.63 | 2.01 |
| Gold | Au | 79 | 196.97 | 2.54 |
| Hafnium | Hf | 72 | 178.49 | 1.30 |
| Hassium | Hs | 108 | [269] | |
| Helium | He | 2 | 4.003 | 0.00 |
| Holmium | Ho | 67 | 164.93 | 1.23 |
| Hydrogen | H | 1 | 1.008 | 2.20 |
| Indium | In | 49 | 114.82 | 1.78 |
| Iodine | I | 53 | 126.9 | 2.66 |
| Iridium | Ir | 77 | 192.22 | 2.20 |
| Iron | Fe | 26 | 55.84 | 1.83 |
| Krypton | Kr | 36 | 83.8 | 3.00 |
| Lanthanum | La | 57 | 138.91 | 1.10 |
| Lawrencium | Lr | 103 | [262] | |
| Lead | Pb | 82 | 207.2 | 2.33 |
| Lithium | Li | 3 | 6.941 | 0.98 |
| Livermorium | Lv | 116 | [293] | |
| Lutetium | Lu | 71 | 174.97 | 1.27 |
| Magnesium | Be | 12 | 24.31 | 1.31 |
| Manganese | Mn | 25 | 54.94 | 1.55 |
| Meitnerium | Mt | 109 | [278] | |
| Mendelevium | Md | 101 | [258] | 1.30 |
| Mercury | Hg | 80 | 200.59 | 2.00 |
| Molybdenum | Mo | 42 | 95.94 | 2.16 |
| Moscovium | Mc | 115 | [289] | |
| Neodymium | Nd | 60 | 144.24 | 1.14 |
| Neon | Ne | 10 | 20.18 | |
| Neptunium | Np | 93 | [237] | 1.36 |
| Nickel | Ni | 28 | 58.69 | 1.91 |
| Nihonium | Nh | 113 | [286] | |
| Niobium | Nb | 41 | 92.91 | 1.60 |
| Nitrogen | N | 7 | 14.01 | 3.04 |
| Nobelium | No | 102 | [259] | 1.30 |
| Oganesson | Og | 118 | [294] | |
| Osmium | Os | 76 | 190.23 | 2.20 |
| Oxygen | O | 8 | 16 | 3.44 |
| Palladium | Pd | 46 | 106.42 | 2.20 |
| Phosphorus | P | 15 | 30.97 | 2.19 |
| Platinum | Pt | 78 | 195.08 | 2.28 |
| Plutonium | Pu | 94 | [244] | 1.28 |
| Polonium | Po | 84 | [209] | 2.00 |
| Potassium | K | 19 | 39.1 | 0.82 |
| Praseodymium | Pr | 59 | 140.91 | 1.13 |
| Promethium | Pm | 61 | [145] | |
| Protactinium | Pa | 91 | 231.04 | 1.50 |
| Radium | Ra | 88 | [226] | 0.90 |
| Radon | Rn | 86 | [222] | |
| Rhenium | Re | 75 | 186.21 | 1.90 |
| Rhodium | Rh | 45 | 102.91 | 2.28 |
| Roentgenium | Rg | 111 | [281] | |
| Rubidium | Rb | 37 | 85.47 | 0.82 |
| Ruthenium | Ru | 44 | 101.07 | 2.20 |
| Rutherfordium | Rf | 104 | [267] | |
| Samarium | Sm | 62 | 150.36 | 1.17 |
| Scandium | Sc | 21 | 44.96 | 1.36 |
| Seaborgium | Sg | 106 | [269] | |
| Selenium | Se | 34 | 78.96 | 2.55 |
| Silicon | Si | 14 | 28.09 | 1.90 |
| Silicon | Si | 14 | 28.09 | 1.90 |
| Silver | Ag | 47 | 107.87 | 1.93 |
| Sodium | Na | 11 | 22.99 | 0.93 |
| Strontium | Sr | 38 | 87.62 | 0.95 |
| Sulfur | S | 16 | 32.07 | 2.58 |
| Tantalum | Ta | 73 | 180.95 | 1.50 |
| Technetium | Tc | 43 | [98] | 1.90 |
| Tellurium | Te | 52 | 127.6 | 2.10 |
| Tennessine | Ts | 117 | [294] | |
| Terbium | Tb | 65 | 158.93 | |
| Thallium | Tl | 81 | 204.38 | 1.62 |
| Thorium | Th | 90 | 232.04 | 1.30 |
| Thulium | Tm | 69 | 168.93 | 1.25 |
| Tin | Sn | 50 | 118.71 | 1.96 |
| Titanium | Ti | 22 | 47.87 | 1.54 |
| Tungsten | W | 74 | 183.84 | 2.36 |
| Uranium | U | 92 | 238.03 | 1.38 |
| Vanadium | V | 23 | 50.94 | 1.63 |
| Xenon | Xe | 54 | 131.29 | 2.60 |
| Ytterbium | Yb | 70 | 173.04 | |
| Yttrium | Y | 39 | 88.91 | 1.22 |
| Zinc | Zn | 30 | 65.39 | 1.65 |
| Zirconium | Zr | 40 | 91.22 | 1.33 |
Sources: PinterPandai, Chemicool, Live Science, Royal Society of Chemistry
Photo credit: Pixabay