Otorhinolaryngology Oto-rhino-laryngology
Otorhinolaryngology treats diseases of the head and neck, and more specifically of the ear (oto), nose (rhino) and throat (larynx). This specialty, commonly called ENT, therefore focuses on the ear – external (pavilion, auditory canal), middle (eardrum) and internal –, the nose and the sinuses, the throat (mouth, tongue, larynx, pharynx, trachea), salivary glands and thyroid.
Otolaryngology consists of several branches, namely:
- Otology: the study of the ear and ear abnormalities and microsurgery.
- Rhinology: the science of the nose and paranasal sinuses, so nowadays they are often also called rhinology and sinusology
- Laryngopharynx: the science of the throat
- Head and neck surgical oncology: the subsection dealing with tumors in the ENT (ears, nose and throat) Head and neck
When to make an appointment with an ENT?
The attending physician usually refers his patient to an ENT when he complains of being bothered by:
- Extraneous noises (tinnitus of non-vascular origin)
- Hearing loss or continuous pain in the ear
- Suffering from repeated angina (chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart)
- Rhinitis and other nasopharyngitis
- Difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia)
- Voice is abnormally altered (dysphonia)
- Suffering from dizziness or sleep disturbances.
- Each organ of the head and neck can be variously affected – malformation, inflammation, ENT tumour, paralysis, degeneration…
The reasons for consulting an ENT specialist are multiple and concern all ages of life.
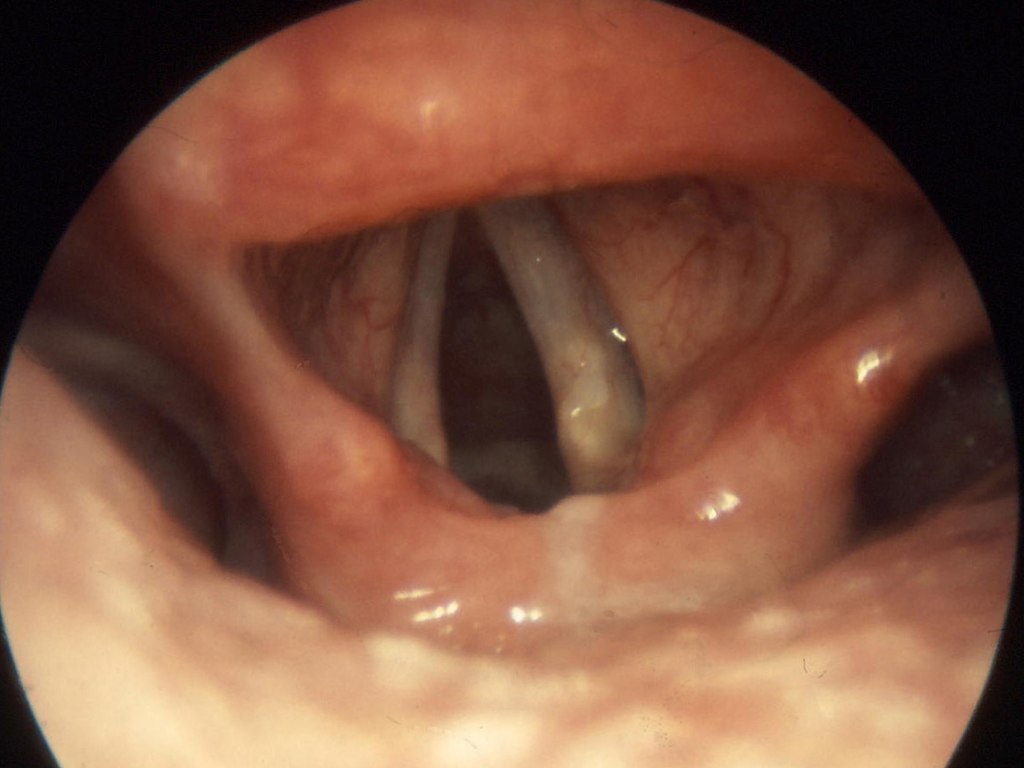
The vocal cords seen in fiber optic endoscopy. I, Welleschik, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
What does an ENT treat?
Infections and inflammations affecting these organs remain the most frequent reasons for consultation: otitis, mastoiditis, rhinitis, sinusitis, nasopharyngitis, angina, tonsillitis… With the current addition of an additional specialization – oto-neuro-surgery, oncology, plastic surgery, phoniatrics, audiometry… – ENT covers the entire head and neck.
As a cervicofacial (relating to, or affecting the neck and face) surgeon, he performs, among other things, the removal of tonsils (tonsillectomy) and adenoidectomy (adenoidectomy). He operates on the mastoid, sinuses and congenital malformations (oesophageal atresia), excision of tumors (thyroid nodules, tumors of the tongue and mouth). They repairs trauma and injuries, places prostheses, implants and uses microsurgery to improve hearing.
They are also involved in the field of aesthetics: rhinoplasty, eyelid and chin surgeries, etc. The ENT specialist is also the specialist in vertigo and balance problems, when they are related to the ear (inner ear disorders, vestibular neuritis, Ménière’s disease). They often acts in close collaboration with the endocrinologist (thyroid gland disorders), the oncologist (malignant tumors) or the pulmonologist (snoring, sleep apnea). Read also: Why do we sleep badly in a new place? first night effect

Otolaryngologist (laryngologist) examining a child’s ear. Basilio de Jesus, Media Presidency of East Timor (M-PR), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Sources: PinterPandai, American Hospital of Paris, Concilio, NHS UK
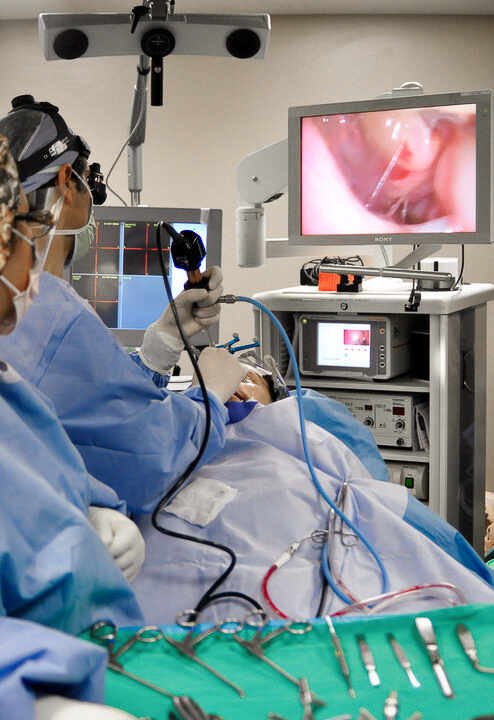
Photo credit: BestInPlastics (CC BY-SA 3.0) © Photographer – James C. Mutter / Otolaryngologist Mani Zadeh, MD via Wikimedia Commons
Photo description: Otolaryngologist performing an endoscopic sinus surgical procedure.