Hemorrhoids: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen veins in the lower rectum or anus that can cause discomfort, pain, and bleeding. They are a common condition affecting millions of people worldwide, with men and women equally affected. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for hemorrhoids.
Symptoms:
The most common symptoms of hemorrhoids include:
- Pain or discomfort in the anal region
- Swelling or inflammation in the anus
- Itching or irritation around the anus
- Bleeding during bowel movements
- Painless lumps or bumps around the anus
- Leakage of fecal matter or mucus
The severity of these symptoms can vary depending on the size and location of the hemorrhoids. Internal hemorrhoids are located inside the rectum and may not cause noticeable symptoms unless they become enlarged or prolapsed. External hemorrhoids, on the other hand, are located outside the anus and can be painful and uncomfortable.
Causes:
Hemorrhoids can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Straining during bowel movements
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea
- Obesity or being overweight
- Pregnancy or childbirth
- Sitting or standing for long periods
- Heavy lifting or exertion
- Aging
These factors can put pressure on the veins in the anus and rectum, causing them to become swollen and inflamed. Hemorrhoids can also be genetic or occur as a result of medical conditions such as liver disease or inflammatory bowel disease.
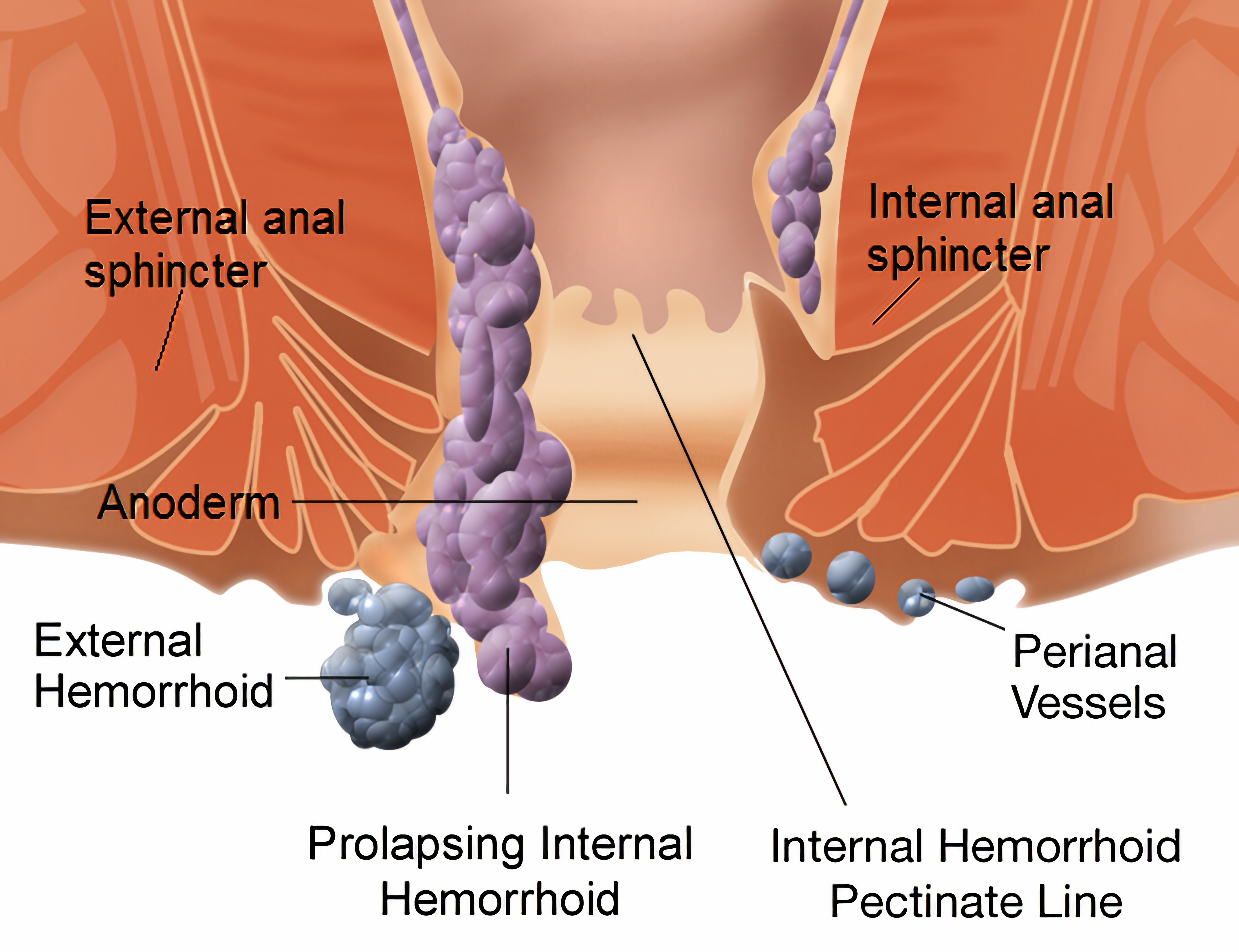
Diagram demonstrating the anatomy of both internal and external hemorrhoids. WikipedianProlific and Mikael Häggström, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Treatment of Hemorrhoids:
Treatment for hemorrhoids depends on the severity of the condition and the symptoms experienced. Mild cases of hemorrhoids can often be treated with home remedies, such as:
- Eating a high-fiber diet and drinking plenty of fluids
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications
- Using topical creams or ointments to reduce itching and inflammation
- Soaking in warm water (sitz baths) to relieve discomfort and promote healing
For more severe cases, medical treatment may be necessary. These treatments can include:
- Rubber band ligation: A small rubber band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply, causing it to shrink and fall off.
- Sclerotherapy: A chemical solution is injected into the hemorrhoid to shrink it.
- Infrared coagulation: A special device is used to heat and shrink the hemorrhoid.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgery to remove the hemorrhoids.

Internal hemorrhoid grades. Grade I: No prolapse, just prominent blood vessels.
Grade II: Prolapse upon bearing down, but spontaneous reduction.
Grade III: Prolapse upon bearing down requiring manual reduction.
Grade IV: Prolapse with inability to be manually reduced. Prof. Dr. A. Herold, End- und Dickdarm-Zentrum Mannheim, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
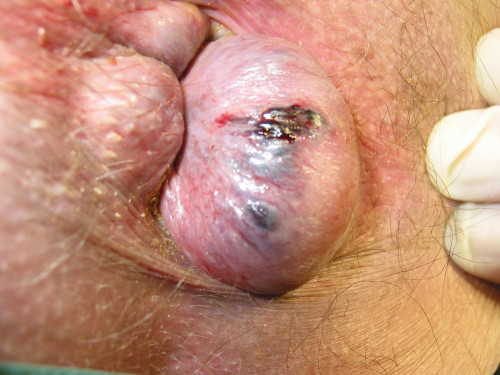
External hemorrhoids occur below the dentate (or pectinate) line. They are covered proximally by anoderm and distally by skin, both of which are sensitive to pain and temperature. Dr. K.-H. Günther, Klinikum Main Spessart, Lohr am Main, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Prevention:
To prevent hemorrhoids from developing or worsening, you can take the following steps:
- Eat a high-fiber diet and drink plenty of fluids
- Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid sitting or standing for long periods
- Take breaks and move around if you have to sit or stand for extended periods
- Use a stool softener or laxative if you have chronic constipation
- Practice good hygiene and avoid using harsh soaps or toilet paper
Conclusion:
Hemorrhoids are a common and often uncomfortable condition that can be treated effectively with a variety of methods. If you experience symptoms of hemorrhoids, it is important to seek medical advice to determine the best course of treatment for your condition. With proper care and prevention measures, you can reduce your risk of developing hemorrhoids and maintain good digestive health.
Information: Cleverly Smart is not a substitute for a doctor. Always consult a doctor to treat your health condition.
Sources: PinterPandai, Cleaveland Clinic, Belmarra Health, Aloe vera, Anal itching, Harvard, Baishideng Publishing Group Inc., Mayo Clinic, NIDDK, Healthline (coconut oil)
Photo credit: derneuemann via Pixabay



