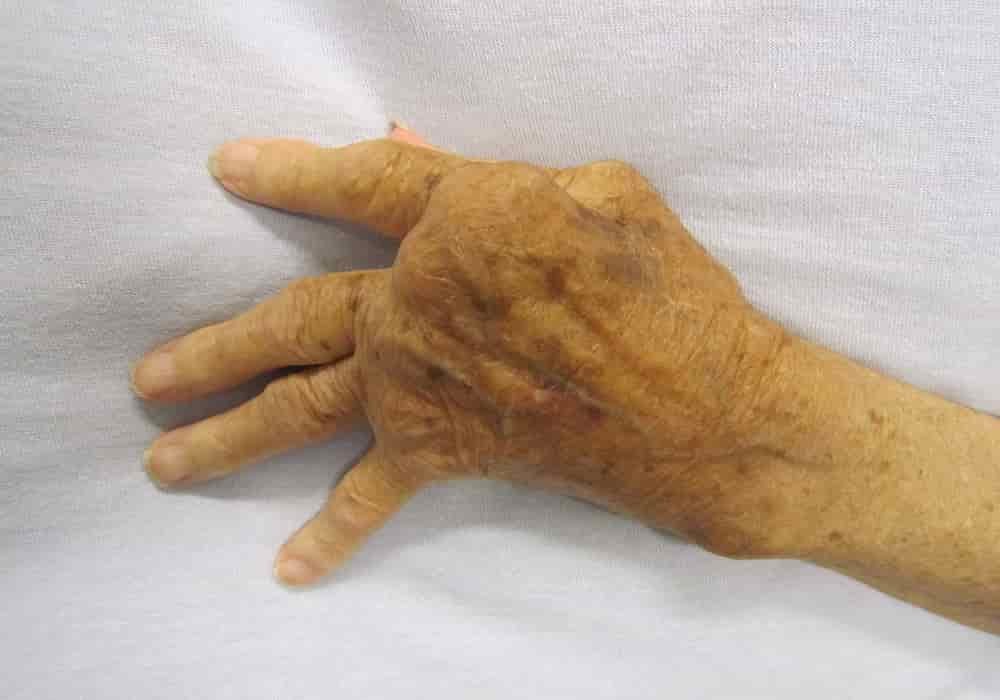
Are Rheumatism and Gout the Same Disease?
Although Rheumatism and Gout look similar and have the same symptoms, namely making joints painful, red, and swollen, actually rheumatism and gout are different diseases. Rheumatism in medical language is called rheumatoid arthritis, which is a type of autoimmune disease that makes joints stiff and inflamed.
Inflammation resulting from the symptoms of rheumatism is caused by a compromised immune system. So, the immune system actually attacks the body’s healthy joint tissue to make it damaged.
Do Rheumatism and Gout Have the Same Cause?
Rheumatoid arthritis and gout are types of arthritis, but the underlying causes are very different. Rheumatism is an autoimmune condition. It occurs when your immune system attacks the tissue that lines your joints. These attacks cause painful swelling, inflammation, and joint deformity. Because rheumatoid arthritis is an immune system disease (your doctor will call it an autoimmune condition), it can also affect other parts of the body, including the skin, eyes, and heart. Gout affects people with too much uric acid in their blood. Your body creates this type of acid when it “breaks down” certain foods, including meat. Your kidneys can usually excrete it when you urinate. But when too much of it is in your system, uric acid can form crystals. These needle-like crystals accumulate in the joints and surrounding tissues, causing pain and swelling.

Gout Symptoms
Meanwhile, joint pain due to gout symptoms is caused by too much uric acid in the body. As explained above, high uric acid levels in the body occur due to consuming foods that contain purines. In the body, purines will be processed into uric acid and under normal circumstances, the body will expel it through feces. However, if the amount is too much, this substance will accumulate and turn into crystals in the joints, then inflammation occurs.
Symptoms of the difference between rheumatism and gout
Here are the symptoms of the difference between rheumatism and gout that you should recognize:
Pain due to gout symptoms usually attacks one joint at a time. This pain is also more common in the feet and toes, especially the big toe joint. While the symptoms of rheumatism can cause pain in any part of the body and can attack several joints at once.
Symptoms of gout are always accompanied by swelling, redness, and pain that often appears. While the symptoms of rheumatism also always cause pain, it doesn’t always show swelling or redness in the joints.
Joint pain due to rheumatic symptoms can vary in intensity, sometimes from mild to severe pain. Meanwhile, pain due to gout symptoms tends to be frequent and severe.
However, the best and most accurate way to find out if you have gout or rheumatism is to see a doctor. The doctor will also help you with the necessary medications and treatments.
Definition of Rheumatism or Arthritis (Rheumatoid Arthritis)
Rheumatism is an autoimmune disease that causes joints to become inflamed, stiff, painful, and swollen. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic progressive disease causing inflammation in the joints and resulting in painful deformity and immobility, especially in the fingers, wrists, feet, and ankles.
If left untreated, it can cause permanent damage that can interfere with your quality of life. According to the American College of Rheumatology, about 1.3 million Americans have RA.
RA is also a systemic disease. This means it can affect other organs of the body such as the eyes, skin, lungs, and heart. People who have RA are at higher risk of heart disease than those who don’t.
Definition of Uric Acid (Gout)
Gout (gout) is a very painful type of arthritis that usually affects the big toe joint. It can also affect the tops of the feet and ankles. Occasionally, it is known to attack other joints in the body.
The Greek philosopher-physicist Hippocrates referred to gout as “the arthritis of the rich” because it was historically associated with indulging in rich food and drink.
Difference Between Rheumatism and Gout
Both diseases cause redness, swelling, and pain in the joints. Both can cause serious disability and interfere with your quality of life.
However, a close look at the early signs and which joints are involved will clearly differentiate these two diseases. The best way to tell if you have RA or gout is to make an appointment with your doctor for a diagnosis.
Specific signs that distinguish the difference between rheumatism and gout:
Rheumatism (arthritis)
The pain can be mild, moderate or severe and is usually associated with stiffness.
It can affect joints and is usually symmetrical on both sides of the body.
It most commonly occurs in the small joints of the hands, wrists, and feet.
Joints may become painful, red, and swollen.
Uric Acid (Gout)
It usually occurs in the feet, most commonly at the base of the big toe.
Redness, swelling, and intense pain.
Causes of Rheumatism and Gout
Rheumatism (arthritis)
The medical community does not yet know what causes rheumatism. Scientists think part of it has to do with a person’s genetic makeup and the condition is triggered by something in the environment, like a virus.
Uric Acid (Gout)
Rich foods and drinks can cause gout indirectly. But the root cause is purines. These chemical compounds are found in certain foods.
Foods rich in purines include most meats (especially organ meats), most fish and shellfish, and even some vegetables. Whole grain breads and cereals also contain purines.
The body converts purines into uric acid. Gout can occur whenever there is too much uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is normally excreted in the urine, but high levels can form sharp crystals in the joints, causing inflammation and severe pain.
Rheumatism and Gout Treatment
Rheumatism (arthritis)
Rheumatism cannot be cured. Treatment focuses on controlling joint inflammation, relieving symptoms, and reducing damage to the joints. Your doctor will work with you to create a treatment plan that fits your needs.
Active and severe rheumatism is usually treated with “disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs” or strong biologics. The latter are genetically engineered compounds designed to attack certain cells or chemicals involved in the immune process. They work to slow or stop disease progression and can relieve inflammation and pain.
Mild to moderate rheumatism is treated with non-biological “disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs”. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also used to treat pain and inflammation, often in addition to “disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs”.
Uric Acid (Gout)
In addition to medications, your doctor may recommend dietary changes.
Medications that treat gout include:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Medications containing nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as indomethacin or naproxen (Naprelan, Naprosyn).
Medications containing corticosteroids, such as prednisone (Rayos).
Medications containing colchicine (Colcrys), are given with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to treat acute attacks or prevent future attacks.
Drugs that inhibit the production of uric acid crystals.
Uric Acid Characteristics
The most common features of gout are:
1. Severe joint pain
Joint pain is one of the common symptoms that appear when uric acid levels in the blood are high.
These symptoms occur because the kidneys are not able to process uric acid that is already too much. Untreated uric acid can then build up in joints and harden into crystals. This crystallization causes the joints to become inflamed and painful.
The joints most often experience pain due to gout are the big toe, knee, ankle, elbow, and thumb.
Joint pain can occur suddenly. Joint pain as a feature of gout is more common at night while sleeping.
2. Joint swelling and tenderness
The characteristics of joint pain due to gout can also be seen from the appearance of problematic joints. Joints that are problematic due to symptoms of high uric acid will look swollen and feel soft when pressed.
This tender swelling occurs for two reasons. One is because the joint lining tissue called the synovium swells, and the second is because the amount of synovial fluid (joint lubricant) increases.
Both of these conditions indicate that there is an active inflammatory process in which white blood cells enter the joint a lot.
3. The skin on the painful joints is reddish
If the problematic joint is not only swollen and painful but the skin is also bright red, this could be a sign of gout.
In normal amounts, uric acid will be excreted through urine. But when the body produces too much uric acid, the kidneys will have difficulty processing it. The excess can accumulate, then form a cristal in the joint. This causes inflammation.
When there is inflammation in the joints, blood flow will increase going towards the affected joint, this is called vasodilation. Eventually the skin on the joint will turn red.
4. Hot/warm feeling around the joints
Symptoms of gout can also cause swollen and red joints to feel hot. The sensation of heat that appears in these joints is the effect of the inflammatory process.
The inflammatory process, aka inflammation, will trigger the body’s immune system to release small proteins (peptides) into the soft tissues around the joints. Substances that cause inflammation also cause fluid around the joints to collect.
This increases blood flow, causing the joints to swell and feel warm.
Less common features of gout
Gout has many common features. However, symptoms will usually appear based on the severity and complications that occur.
Here are some of the less common symptoms that can strike you at any time due to high uric acid levels:
1. Flu-like symptoms
The inflammation experienced with gout can usually become quite severe if left untreated. Uniquely, the symptoms of inflammation due to high uric acid can appear similar to the flu. In addition to joint pain, sometimes gout attacks can also be accompanied by high fever, muscle aches, and fatigue.
These flu-like symptoms are caused by the body’s immune system releasing white blood cells and special antibodies to fight the inflammation. This response actually does not have to exist in gout sufferers because this disease is not caused by viruses or bacteria. But sometimes, the immune system does trigger an inflammatory response when there’s nothing to fight back.
After that, your immune system destroys its own tissues because it’s as if there is a foreign substance that needs to be fought. The result, will be similar to symptoms of fever or flu caused by viral and bacterial inflammation.
2. Having kidney stones
Symptoms of severe high uric acid include the formation of kidney stones. This is because high uric acid will accumulate in the blood and form crystals in the kidneys. Crystals can become large stones and can be very painful. Kidney stones that form as a symptom of gout can cause kidney damage or failure.
3.Tophi
Another characteristic of severe gout is the deposition of uric acid crystals under the skin.
These deposits will appear as small white or yellow lumps (nodules) under the skin of the joints, including the toes, knees, and elbows. However, nodules can also appear anywhere on your body, including the spinal canal. Lumps characteristic of uric acid is called tophi.
Tophi, which is a sign of gout, is usually painless. But in some cases, the lump can become inflamed and ooze fluid. Tophi nodules that are large and painful may need to be surgically removed.
4. Sacroiliac joint pain in the pelvis
The characteristics of gout pain are generally felt in the feet or specifically in the big toe.
However, there are also symptoms of gout that appear in another joint called the sacroiliac. These joints are located on either side of the pelvis between the sacrum and ilium.
Symptoms of high uric acid that attacks the sacroiliac joints can cause low back pain (lower back) or hip pain.
5. Wrist pain
Wrist joint pain can also be a feature of gout. This condition is known as gout polyarticulari, which means that your disease has affected more than one joint.
The diagnosis of polyarticular gout due to gout is usually difficult to confirm. then the doctor needs a laboratory examination by taking a sample of your joint first.
Symptoms of gout by stages
Symptoms or characteristics of gout usually appear suddenly, unpredictable, and often occur in the middle of the night. Most of the symptoms or characteristics of gout only occur within a few hours for 1-2 days.
However, in severe cases, joint pain can last for weeks. If you experience these symptoms, then the disease you have is quite severe. There are also those who feel the characteristics of gout for up to 6-12 months in different intensities every day.
3 stages of gout based on its severity
1. First stage
The characteristics of gout can already be seen from high uric acid levels in the blood.
However, no gout symptoms have appeared. You may never feel the symptoms of gout.
Usually, people who have this disease will feel the symptoms of gout for the first time after they are attacked by kidney stones.
2. Second stage
Entering the second stage, uric acid levels that are too high have formed crystals on the toes.
The characteristics of gout that you can feel at this stage are pain, swelling, and redness in the joints, but it won’t last long.
After some time, you will experience other symptoms of high uric acid with increasing intensity and frequency.
3. Third stage
In the third stage, the symptoms of gout do not go away and the uric acid crystals that form do not just accumulate in one joint. At this stage will appear lumps that have crystallized under the skin. This condition causes more severe pain and can damage cartilage.
Most people who suffer from this disease only experience stages one or two. Quite rarely people suffering from gout are found to have reached the third stage. In general, most people with gout symptoms can be treated well in the second stage.
Rheumatism and Gout: Getting the Correct Diagnosis
1. The Role of Blood Test
In the absence of a definitive blood test available for rheumatism, doctors instead look for certain antibodies in the blood that indicate their presence, such as antinuclear antibodies, rheumatoid factor, and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP: anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide). Your rheumatologist will also order a complete blood count to see if you have anemia, which is common in people with rheumatism.
Rheumatism is more difficult to identify than gout because measuring the amount of uric acid in the blood is considered a definitive test for gout. However, uric acid levels are actually lower during a gout attack, so your doctor will want to repeat the test when symptoms subside.
Normal uric acid levels in the blood
It is 2.5-7.5 mg/dL for women and 4-8.5 mg/dL for men. When measured from urine, normal adult uric acid levels are 250-750 mg per total urine for 24 hours.
2. The Role of Imaging Tests
Both rheumatism and gout can cause joint erosion, so a rheumatologist / doctor will order you to make tests such as X-rays (X-rays) to look for them. X-rays can also detect the onset of tophi (deposits of urate crystals that form under the skin in cases of chronic gout, or tophaceous gout). The patient’s clinical history, physical examination are also an important part of the diagnostic process for gout.
Sources: PinterPandai, Healthline, Medical News Today, NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information), Arthritis Foundation, Web MD